Now that you understand the basic concepts of the workings of a CDP platform, it is time to introduce the high-level workflow of a CDP platform. This will help to create a roadmap for a CDP implementation although we will not be getting into the details of the implementation here.
The high-level workflow of a CDP platform looks as follows:
Step 1: Setting up source systems to send data to the CDP
The first step is to make sure the source system is ready to send data to the CDP. How exactly you make this happens depends on what type of CDP vendor you have chosen and what is your use case.
We will tackle a common scenario here. Most CDPs come with prebuilt connectors, which you can use to connect to different systems. All you need to do is to set up authentication between the two systems and set the criteria for ingesting the data. Then you will be able to ingest data into your CDP. You can also ingest data into CDP from any data lake or data warehouse.
CDPs simplify the process of data ingestion by automating the data connection using pre-built connectors. Alternatively, one can write the code to ingest data from different systems.
For sending event data from apps and websites, one can use SDKs. Client-side systems push data to CDP through SDK implementation.
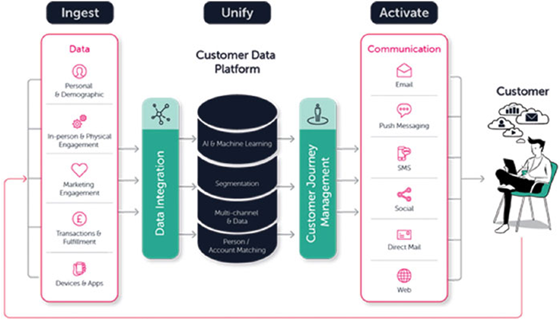
Figure 2.7: We need to set up different systems to send data to CDP (source: https://clever-touch.com/learn/what-makes-a-customer-data-platform-a-customer-data-platform)
Step 2: Data Ingestion
There are different methods by which CDP ingests data from different sources. It also depends on whether you are doing batch ingestion or streaming ingestion.
- Batch ingestion: In batch ingestion, you ingest data as batch files. Batches are units of data that contain one or more files to be ingested as a single unit. Once the data is ingested, batches provide metadata that describes the number of records successfully ingested as well as provide messages for failed records. CSV files are ingested by this method.
- Streaming ingestion: Streaming ingestion allows you to send data from client-and server-side sources to the CDP platform in real-time. The incoming data is instantly made available for use. Stream ingestion is useful for tracking real-time events like website metrics, event data, and so on.
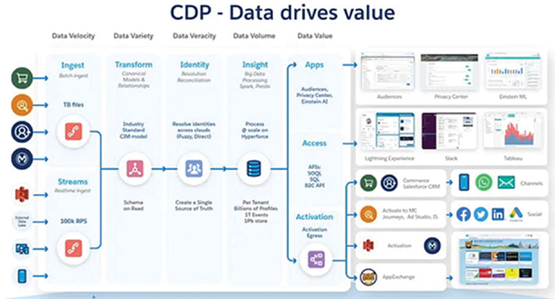
Figure 2.8: You can ingest data in batches or in real-time (source: https://medium.com/salesforce-architects/4-considerations-for-salesforce-cdp-data-ingestion-c00af75167bc)
Step 3: Data Processing and Transformation
The next step is to process and transform the data that we ingested. Based on the end use case, the data needs to be processed and transformed. First and foremost, the data needs to be cleaned and duplicated. Most CDPs have built-in data processing and transformation workflows, which you can choose to simplify the task. You can alternatively write your code to clean and transform the data.
Step 4: Identity Resolution
After making sure that we have clean data in our database, the next step is to perform identity stitching for identity resolution. As explained in the identity resolution section, we use identity graphs to attribute data to a particular user id based on fuzzy matching, deterministic or probabilistic matching.
Most CDPs provide services that help with identity resolution. You can create identity resolution rules to create unique customer profiles. These customer profiles will be useful when you move to the next step.
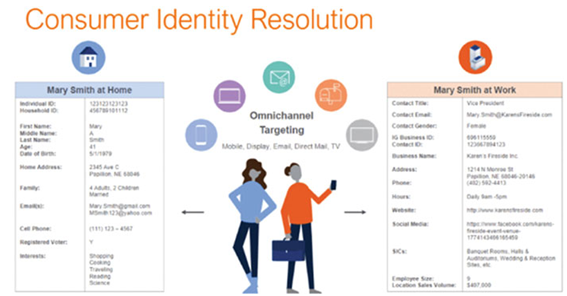
Figure 2.9: Identity resolution (source: https://www.data-axle.com/resources/blog/solving-the-identity-graph-gap-through-robust-identity-resolution/)
Step 5: Segmentation and Activation
Now, this is the time for marketers to segment the customer profiles created through identity resolution. Marketers segment customers based on certain business criteria. After you are done with segmentation, the next step is to publish and activate the segment. Publishing and activating the segment is done through marketing platforms like Google ad manager, Facebook ads manager, or other third-party tools like Blaze. This ensures your marketing campaigns are always targeted toward the right audience. Segmentation and activation are continuous tasks for marketers.
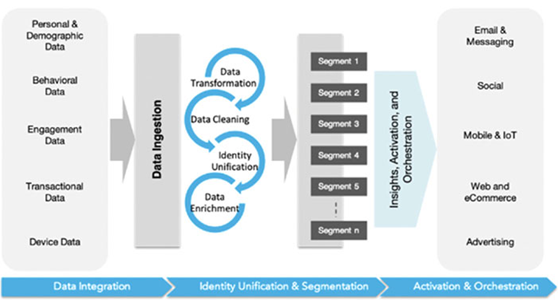
Figure 2.10: Marketers create different segments before activation (source: https://quadrant-solutions.com/market_research/market-outlook-customer-data-platforms-cdp-2019-2024-worldwide/)
The unique customer profiles can also be used for other use cases like product analytics, personalization, and so on. Earlier CDPs were mostly used by marketers to market to the right audience. However, now the customer data is used to push relevant notifications in Android and iOS apps. It is used to personalize the app and web experience based on the user. It is also used to analyze how users are interacting with the product. The use cases are one and many once we get the unique customer profile.
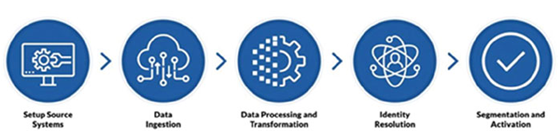
Figure 2.11: CDP workflow
