Now we will understand the high-level working of Salesforce Data Cloud. We have already introduced you to the concepts required for understanding the high-level overview, so let us directly jump into it (Figure 3.13).
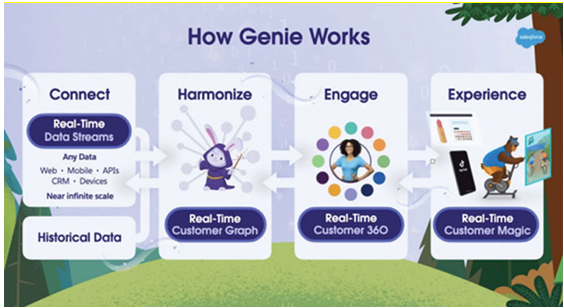
Figure 3.13: Building blocks for Salesforce Data Cloud
Salesforce Data Cloud has four building blocks:
- Connect: Refers to connecting the different sources of data from web, mobile, APIs, CRM, and real-time streaming data. Salesforce Data Cloud can receive data and scale up based on the need.
- Harmonize: Refers to harmonizing the incoming data to form a real-time customer graph.
- Engage: This is the process of creating unified customer profiles through identity resolution and customer segments. We can also create predictive models to help us engage with customers in a more effective way.
- Experience: The process of personalizing the customer experience with the data we have in Data Cloud. The customer segments can be activated through different systems, such as mobile apps, web, ad platforms, and so on. Data Cloud provides real-time personalization at an immense scale.
Next, we will discuss the high-level overview of Salesforce Data Cloud.
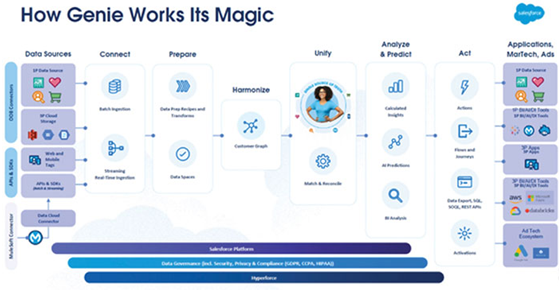
Figure 3.14: Salesforce Data Cloud high-level workflow diagram
In Figure 3.14, you can see the high-level diagram for Salesforce Data Cloud. Let us understand how data moves from one stage to another to finally provide the real-time personalized experience that customers want.
- Setting up the data sources
Salesforce Data Cloud supports several data sources (Figure 3.15). It has some out-of-the-box connectors, which are pre-built integrations that companies can use to quickly set up the connection between two systems. This not only includes the connectors to different Salesforce Applications like Sales Cloud, Service Cloud, and Marketing Cloud but also other popular tools like AWS, Adobe, Google Cloud Studio, and so on. Data Cloud also supports a variety of third-party cloud storage services like data warehouses, databases, and data lakes from AWS, Microsoft, Snowflake, and Google among others. We will discuss later in detail how to set up the connections, but for now, we just need to keep in mind that Data Cloud allows us to easily connect to our data sources.
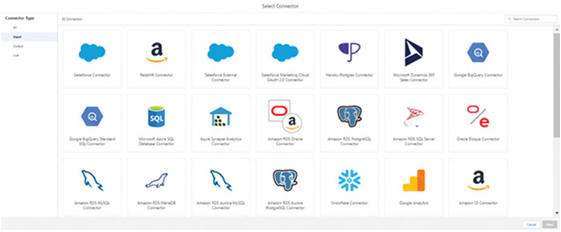
Figure 3.15: Data Cloud provides the ability to connect with different data sources by following a few simple steps
We can also send event analytics data from Android and iOS mobile devices through API connections or SDKs. There are options to send data in batches or stream data to the data cloud platform. Additionally, Mulesoft allows you to connect different data sources to Data Cloud. We will have a detailed discussion on how it can be done in a later chapter.
- Connecting the data sources
After setting up the data sources, the next step is to start ingesting the data, either through batch processing or streaming.
- Prepare the data
The next step is to prepare the data through data cleaning and data transformation. Data Cloud provides an easy-to-use interface to perform data transformation (refer to Figure 3.16), but developers can also write code to perform complex data transformation functions. Most common data transformations are available out of the box and can be used with clicks. Owing to these functionalities, it is easy to perform these transformations even if someone is not a data engineer.
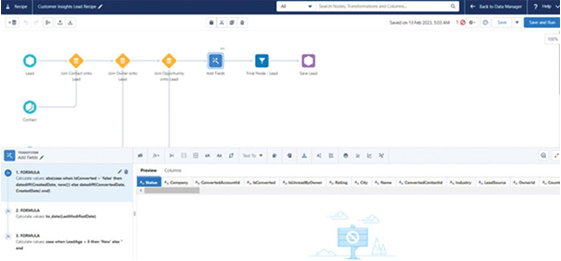
Figure 3.16: Salesforce provides a user-friendly UI for data transformation
